Welcome to the official website of Shanghai Shangshihua Law Firm!



cancel
Clear records
history record
Clear records
history record



Situation introduction:
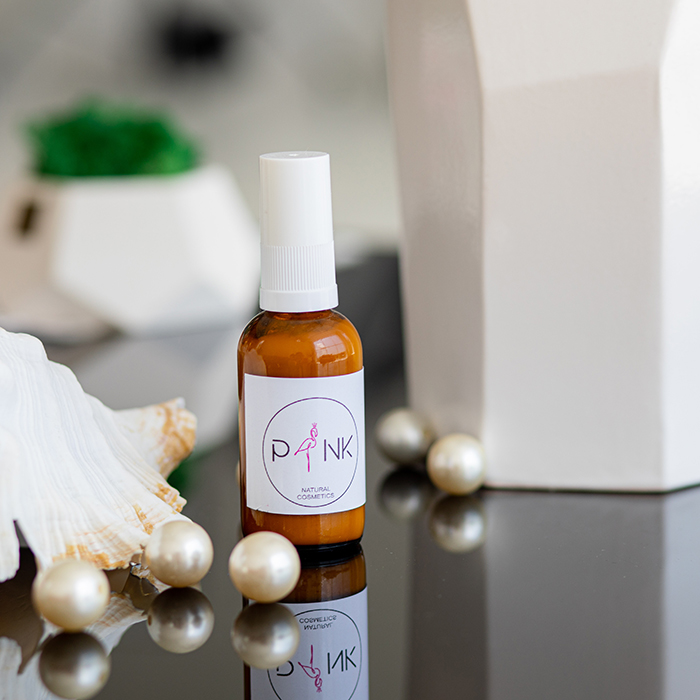
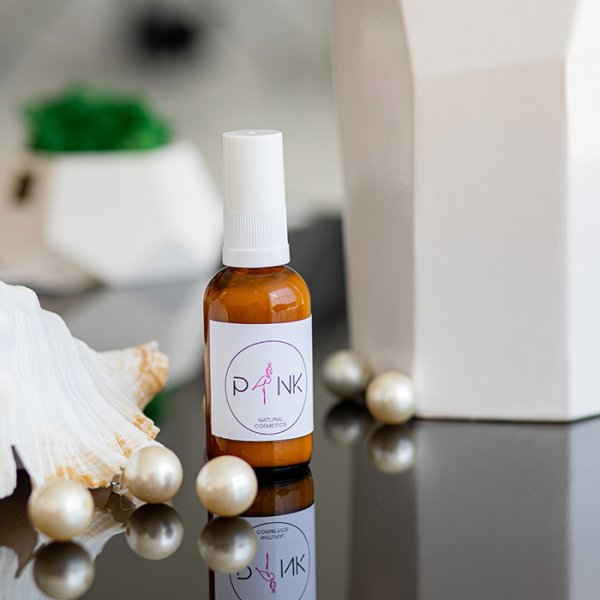
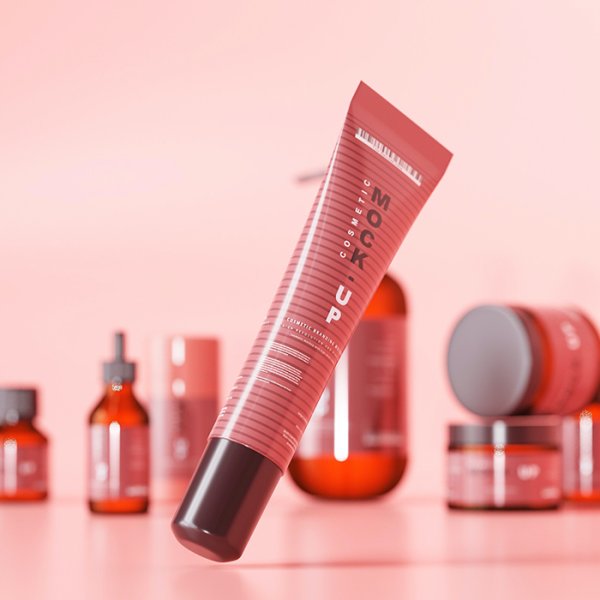
A foreign cosmetics brand has a certain reputation in the field of affordable luxury; it has applied for a registered trademark in English and Chinese in China, and the trademark owner is the company headquarters in the United States; Company A, registered in China, is the general agent of the brand products in China; A The company promotes the brand's products in China, conducts market analysis and advertising, and gradually opens up the market in mainland China. However, a large number of overseas purchasing shops have emerged in the e-commerce market, with lower prices and difficulty in distinguishing authenticity from fake products, which seriously affects the normal market order of this brand in China.
Case analysis:
The characteristics of product sales on e-commerce platforms must use "unique product names" or "registered trademarks" as keywords to attract traffic; overseas purchasing stores are no exception. All stores use Chinese and English trademarks as product names to promote and sell purchasing products. . If overseas purchasing agents are prohibited from using registered trademarks for promotion, Company A’s purpose of preventing overseas purchasing stores from selling goods at unfair prices can be achieved.
implementation plan:
The lawsuit was filed in the People's Court on the grounds that the overseas purchasing agency's use of the registered trademark without the permission of the trademark owner constituted an infringement of the exclusive right to use the registered trademark.
During the course of the lawsuit, some stores claimed that the products they sold were from overseas purchasing agents for resale, and their use of the trademarks was a fair use of the trademarks. However, the judge held that even if the use of the English trademark is fair use, the use of the Chinese trademark still requires the permission of the trademark owner, otherwise it will constitute trademark infringement.
After about a year of continuous rights protection, the impact of overseas purchasing agencies on the domestic market has been basically resolved.
Kind tips:
The litigation authorization document for a domestic agency company from a trademark owner located overseas must be authenticated by the Chinese embassy or consulate in the country where the trademark owner is located; otherwise, it will not have legal effect.
Legal basis:
Article 48 of the Trademark Law The use of trademarks as mentioned in this Law refers to. . . The act of using trademarks in advertising, exhibitions and other commercial activities to identify the source of goods.
Article 57 Anyone who commits any of the following acts shall infringe upon the exclusive right to use a registered trademark: (1) Using the same trademark as the registered trademark on the same product without the permission of the trademark registrant; . . .
Cosmetic Brands - How to protect your rights when buying foreign products at low and random prices
Situation introduction:
A foreign cosmetics brand has a certain reputation in the field of affordable luxury; it has applied for a registered trademark in English and Chinese in China, and the trademark owner is the company headquarters in the United States; Company A, registered in China, is the general agent of the brand products in China; A The company promotes the brand's products in China, conducts market analysis and advertising, and gradually opens up the market in mainland China. However, a large number of overseas purchasing shops have emerged in the e-commerce market, with lower prices and difficulty in distinguishing authenticity from fake products, which seriously affects the normal market order of this brand in China.
Case analysis:
The characteristics of product sales on e-commerce platforms must use "unique product names" or "registered trademarks" as keywords to attract traffic; overseas purchasing stores are no exception. All stores use Chinese and English trademarks as product names to promote and sell purchasing products. . If overseas purchasing agents are prohibited from using registered trademarks for promotion, Company A’s purpose of preventing overseas purchasing stores from selling goods at unfair prices can be achieved.
implementation plan:
The lawsuit was filed in the People's Court on the grounds that the overseas purchasing agency's use of the registered trademark without the permission of the trademark owner constituted an infringement of the exclusive right to use the registered trademark.
During the course of the lawsuit, some stores claimed that the products they sold were from overseas purchasing agents for resale, and their use of the trademarks was a fair use of the trademarks. However, the judge held that even if the use of the English trademark is fair use, the use of the Chinese trademark still requires the permission of the trademark owner, otherwise it will constitute trademark infringement.
After about a year of continuous rights protection, the impact of overseas purchasing agencies on the domestic market has been basically resolved.
Kind tips:
The litigation authorization document for a domestic agency company from a trademark owner located overseas must be authenticated by the Chinese embassy or consulate in the country where the trademark owner is located; otherwise, it will not have legal effect.
Legal basis:
Article 48 of the Trademark Law The use of trademarks as mentioned in this Law refers to. . . The act of using trademarks in advertising, exhibitions and other commercial activities to identify the source of goods.
Article 57 Anyone who commits any of the following acts shall infringe upon the exclusive right to use a registered trademark: (1) Using the same trademark as the registered trademark on the same product without the permission of the trademark registrant; . . .
Related service


 The browser own share function is also very useful~
The browser own share function is also very useful~





